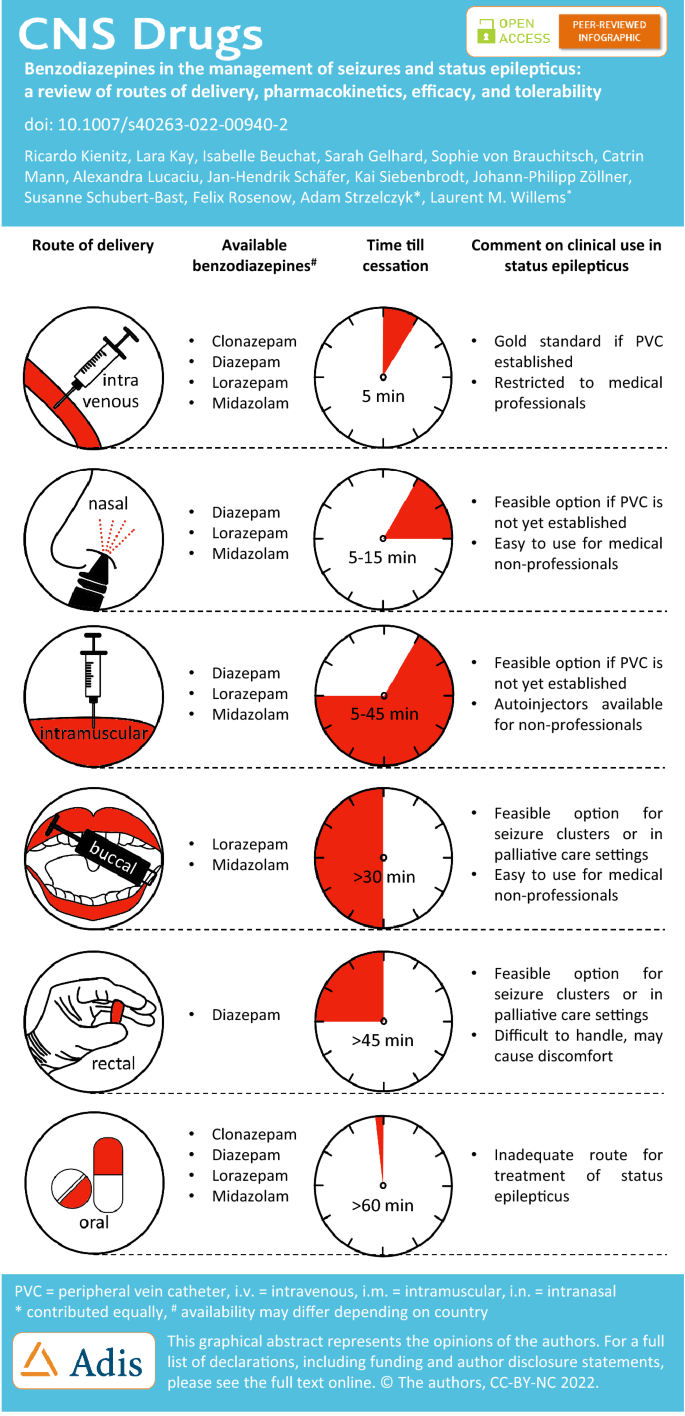
Benzodiazepines in the Management of Seizures and Status Epilepticus: A Review of Routes of Delivery, Pharmacokinetics, Efficacy, and Tolerability | CNS Drugs

Is diazepam or lorazepam the most effective benzodiazepine for use in paramedic management of convulsive seizures in adults? | Journal Of Paramedic Practice
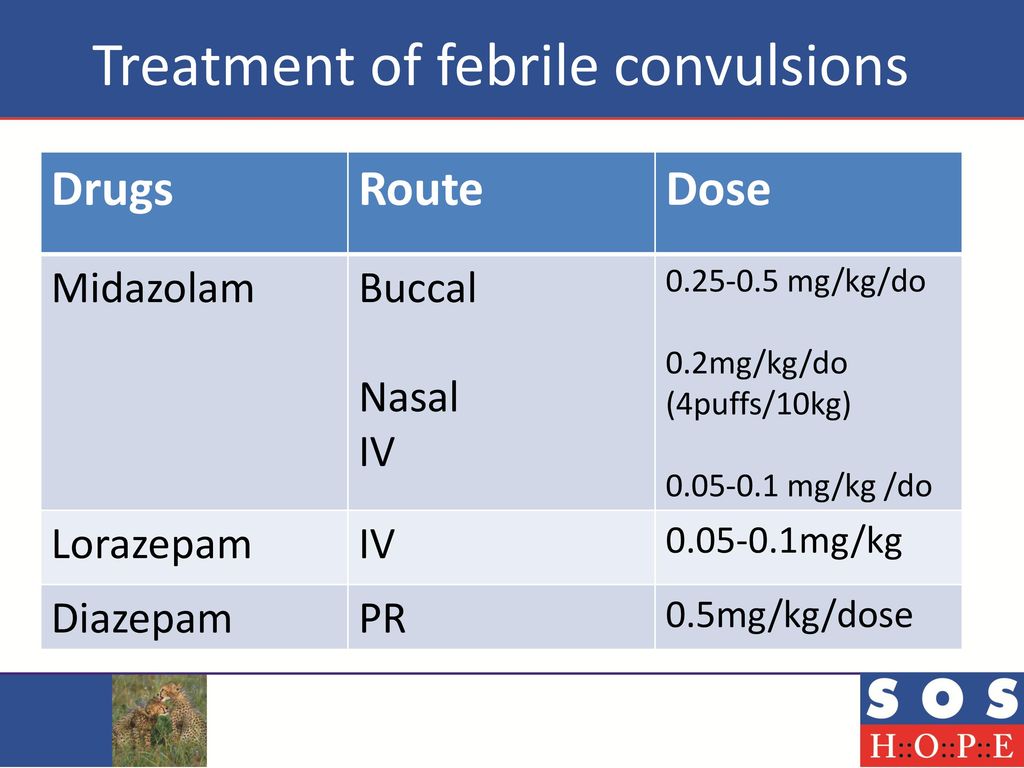
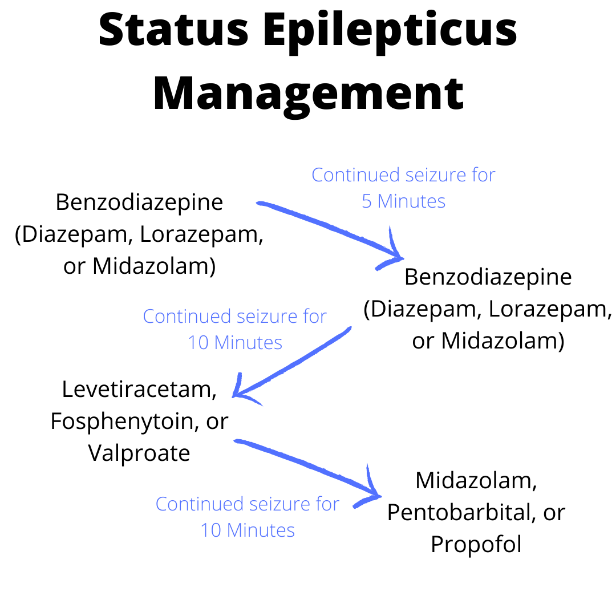
Guideline for the management of convulsive status epilepticus in infants and children | British Columbia Medical Journal
INTRODUCTION - Use of Lorazepam for the Treatment of Pediatric Status Epilepticus: A Randomized, Double-Blinded Trial of Lorazepam and Diazepam - NCBI Bookshelf